The other day I was having a heck of a time trying to figure out how to make a stacked bar chart in Seaborn. But in true open-source/community fashion, I ended up getting a response from the creator of Seaborn via Twitter:
@randyzwitch I don't really like stacked bar charts, I'd suggest maybe using pointplot / factorplot with kind=point
— Michael Waskom (@michaelwaskom) September 4, 2014
So there you go. I don’t want to put words in Michael’s mouth, but if he’s not a fan, then it sounded like it was up to me to find my own solution if I wanted a stacked bar chart. I hacked around on the pandas plotting functionality a while, went to the matplotlib documentation/example for a stacked bar chart, tried Seaborn some more and then it hit me…I’ve gotten so used to these amazing open-source packages that my brain has atrophied! Creating a stacked bar chart is SIMPLE, even in Seaborn (and even if Michael doesn’t like them 🙂 )
Stacked Bar Chart = Sum of Two Series
In trying so hard to create a stacked bar chart, I neglected the most obvious part. Given two series of data, Series 1 (“bottom”) and Series 2 (“top”), to create a stacked bar chart you just need to create:
1
Series 3 = Series 1 + Series 2
Once you have Series 3 (“total”), then you can use the overlay feature of matplotlib and Seaborn in order to create your stacked bar chart. Plot “total” first, which will become the base layer of the chart. Because the total by definition will be greater-than-or-equal-to the “bottom” series, once you overlay the “bottom” series on top of the “total” series, the “top” series will now be stacked on top:
Background: “Total” Series
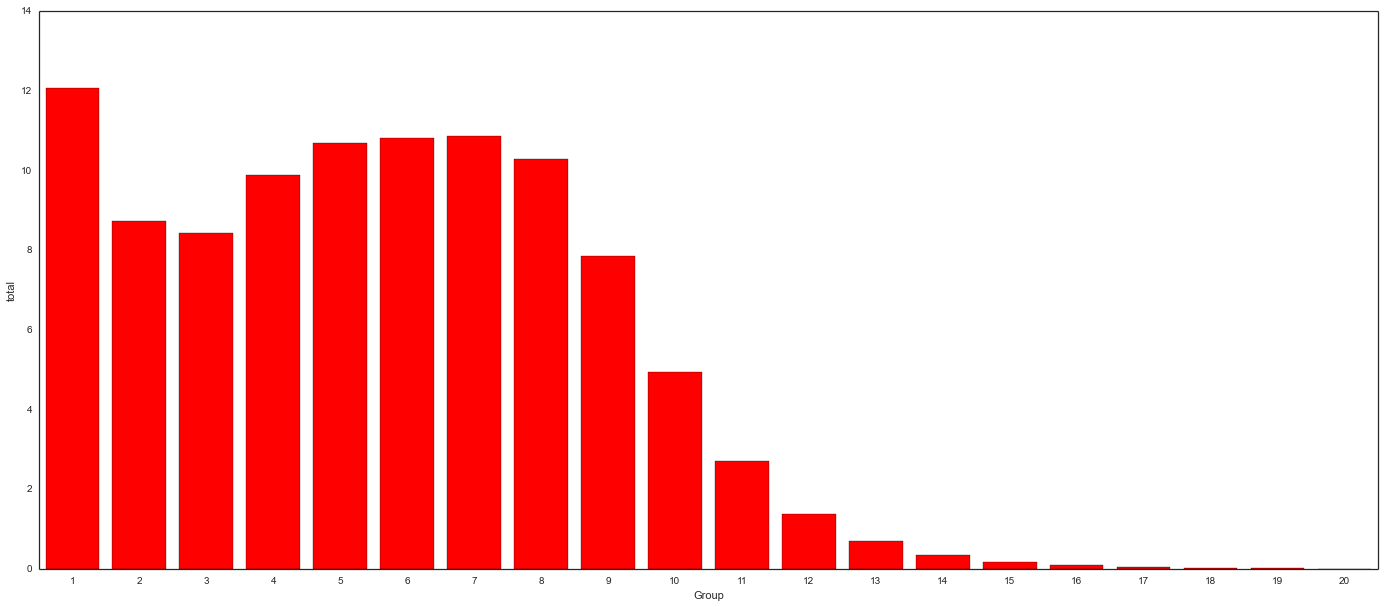
Overlay: “Bottom” Series
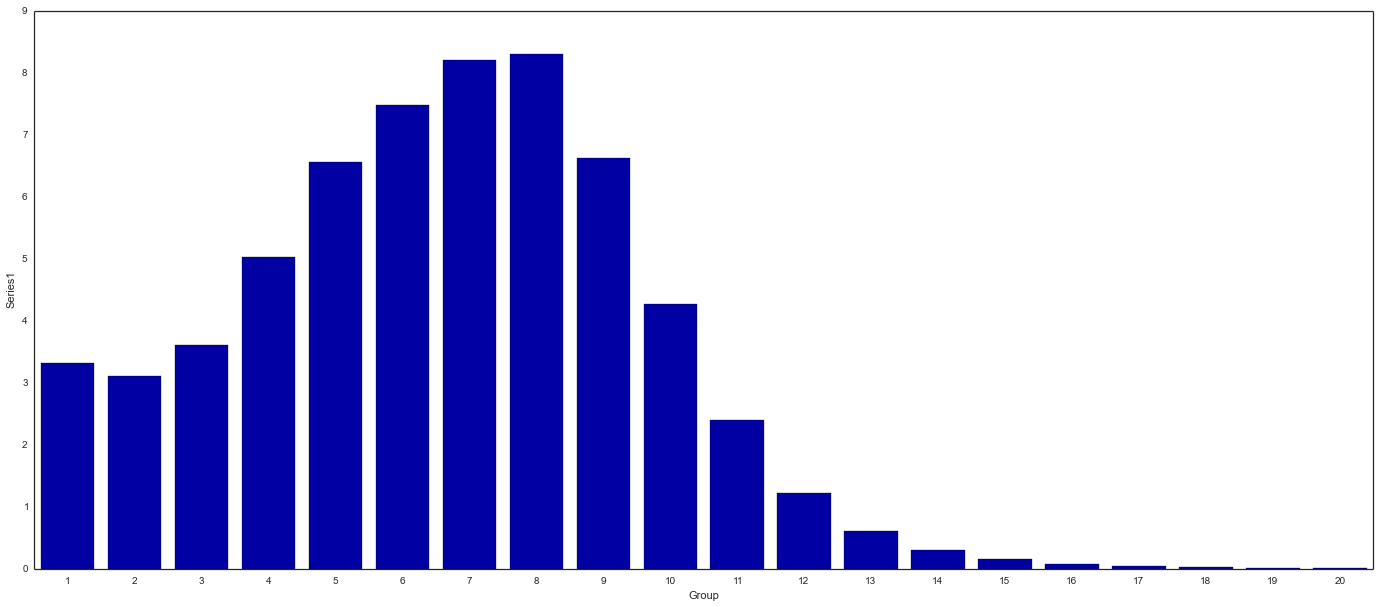
End Result: Stacked Bar Chart
Running the code in the same IPython Notebook cell results in the following chart (download chart data):
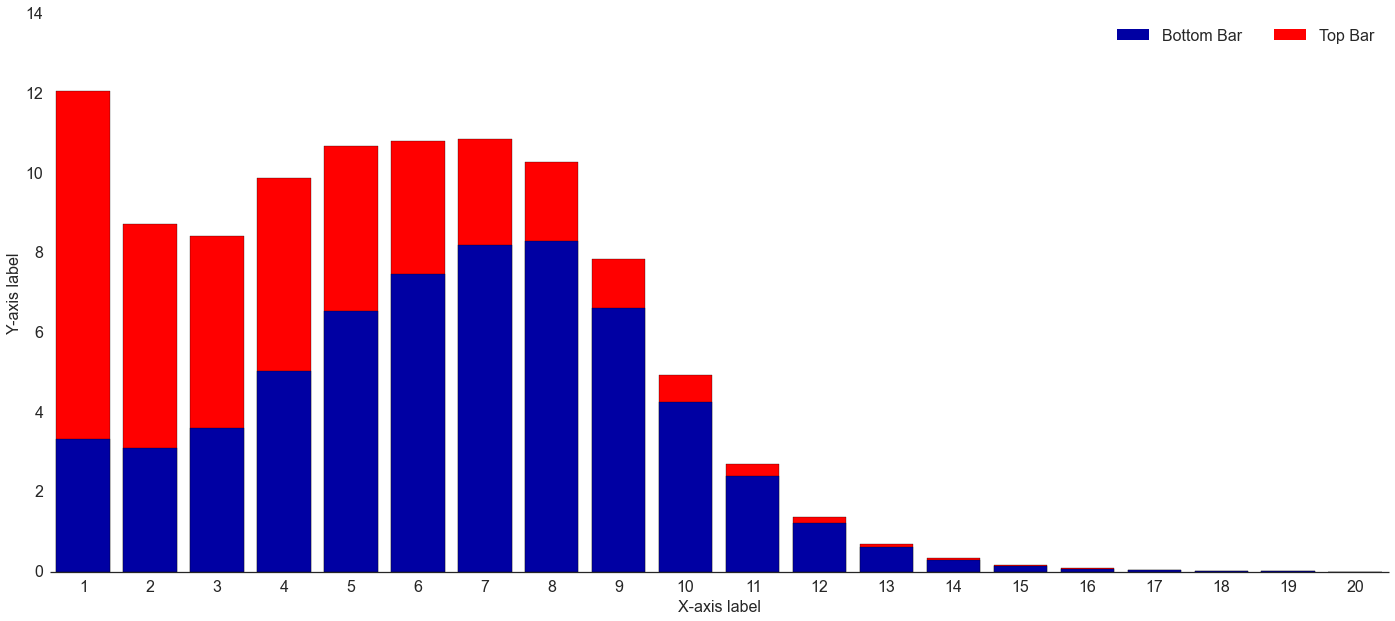
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
#Read in data & create total column
stacked_bar_data = pd.read_csv("C:\stacked_bar.csv")
stacked_bar_data["total"] = stacked_bar_data.Series1 + stacked_bar_data.Series2
#Set general plot properties
sns.set_style("white")
sns.set_context({"figure.figsize": (24, 10)})
#Plot 1 - background - "total" (top) series
sns.barplot(x = stacked_bar_data.Group, y = stacked_bar_data.total, color = "red")
#Plot 2 - overlay - "bottom" series
bottom_plot = sns.barplot(x = stacked_bar_data.Group, y = stacked_bar_data.Series1, color = "#0000A3")
topbar = plt.Rectangle((0,0),1,1,fc="red", edgecolor = 'none')
bottombar = plt.Rectangle((0,0),1,1,fc='#0000A3', edgecolor = 'none')
l = plt.legend([bottombar, topbar], ['Bottom Bar', 'Top Bar'], loc=1, ncol = 2, prop={'size':16})
l.draw_frame(False)
#Optional code - Make plot look nicer
sns.despine(left=True)
bottom_plot.set_ylabel("Y-axis label")
bottom_plot.set_xlabel("X-axis label")
#Set fonts to consistent 16pt size
for item in ([bottom_plot.xaxis.label, bottom_plot.yaxis.label] +
bottom_plot.get_xticklabels() + bottom_plot.get_yticklabels()):
item.set_fontsize(16)
Don’t Overthink Things!
In the end, creating a stacked bar chart in Seaborn took me 4 hours to mess around trying everything under the sun, then 15 minutes once I remembered what a stacked bar chart actually represents. Hopefully this will save someone else from my same misery.